The reason for Japan’s traditional craft export
The rationales for the popularity of Japanese traditional craft export can be classified into the following five categories.
Distinctiveness and Aesthetics
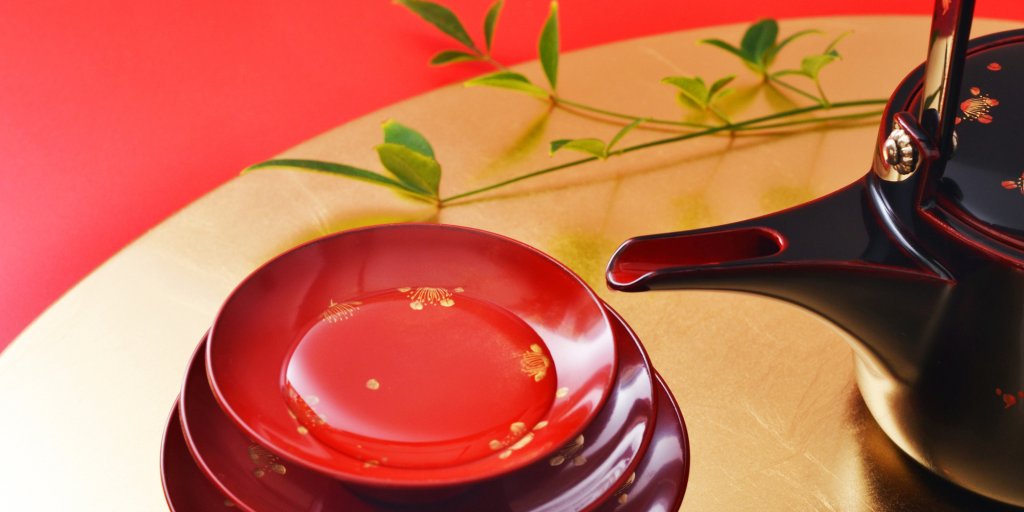
Japanese traditional crafts exhibit exquisite and intricate designs, utilizing techniques and materials that are exclusive to Japan. Such singularities and aesthetics are widely esteemed overseas. Tea ceremony utensils, Japanese paper, lacquerware, ceramics, and woodwork are some examples of crafts that are highly prized abroad.
Heritage and Legacy
Traditional Japanese crafts boast of a long and storied heritage and legacy. These crafts have been passed down through the centuries, leading to the development of exclusive techniques and designs. Foreign nationals take a keen interest in and are drawn to crafts that possess such rich heritage and legacy.
Superiority and Dependability
Traditional Japanese crafts are held in high regard for their superior quality and dependability. These crafts are meticulously crafted by skilled artisans and are subject to stringent quality control. Such quality and dependability are highly valued by people overseas who actively seek out Japanese traditional crafts.
Fostering Cultural Exchange
Japanese traditional crafts also serve as a vehicle for cultural exchange. By means of these crafts, Japanese culture and aesthetics can be effectively conveyed to other countries. Moreover, the interest and learning of foreign nationals in Japanese traditional crafts can lead to deeper cultural exchanges with Japan.
Tourism Potential
Japanese traditional crafts also play a significant role as a tourism resource. Numerous foreign tourists visit Japan with the intention of finding traditional Japanese crafts. Consequently, Japanese traditional crafts are increasingly being recognized as a tourism resource in Japan.
For these reasons, Japanese traditional crafts have garnered immense popularity overseas. These crafts not only convey Japan’s distinctive culture and aesthetics and foster cultural exchange, but also possess a reputation for superior quality and dependability, making them a valuable tourism resource. It is expected that Japanese traditional crafts will continue to draw increasing attention overseas, leading to further dissemination of Japanese culture and technology throughout the world.
Market change that affects traditional craft export
The global demand for traditional Japanese crafts has undergone changes in recent decades, and the reasons for such changes can be attributed to various factors.
One such factor is the changes in global demand, where changes in modern lifestyles have led to a decrease in demand for traditional tableware and furniture, while there has been an increase in demand for Japanese paper and Japanese-patterned fashion items.
Furthermore, the lack of overseas marketing has also had an impact on overseas sales of traditional Japanese crafts. Manufacturers of traditional crafts often encounter difficulties in developing sales channels and promoting their products when entering overseas markets. This has resulted in low awareness of their products abroad and a corresponding low demand.
Export-related issues also pose challenges for Japanese traditional crafts. Strict regulations on manufacturing methods and materials have led to export restrictions on items such as lacquerware, which may be restricted depending on the composition of the lacquer. Additionally, traditional crafts such as ceramics must consider usage and security issues in the exporting country.
Despite these challenges, with changes in demand and improved overseas marketing, it is expected that overseas sales of traditional Japanese crafts will increase in the future.
Traditional craft export Facts
What are the trends in the export value of Japanese traditional crafts for the most recent 20 years? Below is a breakdown of the export value of Japanese traditional crafts for the most recent 20 years (2002 to 2021).
(Billion yen)
2002: 113.6
2003: 114.6
2004: 116.1
2005: 117.8
2006: 123.4
2007: 130.7
2008: 138.5
2009: 118.7
2010: 129.4
2011: 131.3
2012: 132.7
2013: 136.5
2014: 137.1
2015: 146.1
2016: 219.6
2017: 226.7
2018: 228.4
2019: 228.6
2020: 188.2
During the period between 2016 and 2019, there was a gradual yet upward trend in overseas demand for traditional Japanese crafts. However, the year 2020 witnessed a decline in comparison to the preceding year owing to the impact of the novel coronavirus, which led to a drop in retail sales due to the temporary closure of stores and a slump in overseas tourism.
Nevertheless, reports indicate that demand for traditional Japanese crafts abroad has been gradually recovering since the start of 2021. As a result, the export value of these crafts may undergo changes in the future, depending on variations in demand and the emergence of new markets.
What is the composition ratio?
he composition of Japan’s traditional craft exports is as follows
Ceramics: approx. 37
Crafts and ornaments: approx. 21
Lacquerware: approx. 15
Japanese paper: approx. 11
Woodwork: approximately 7
Textiles: approx. 4
Metalwork: approx. 3
Others: about 2%.
Ceramics, being one of the most coveted items among traditional Japanese crafts, are produced in high quantities and are also exported in large volumes due to the heightened demand. The wide range of crafts and accessories, including items made of Japanese paper and fashion items with Japanese patterns, contribute to a relatively high demand for such products. Lacquerware, with its unique manufacturing process and requirement of high technical skill, is considered to be a rare and valuable item, and thus is in high demand. Washi, with the oldest history among Japanese traditional crafts, is characterized by its high quality, further adding to its appeal. The aforementioned factors, such as demand and high quality, influence the composition of traditional craft export items. However, with changes in demand and product diversification, it is expected that the composition ratio will continue to shift in the future.